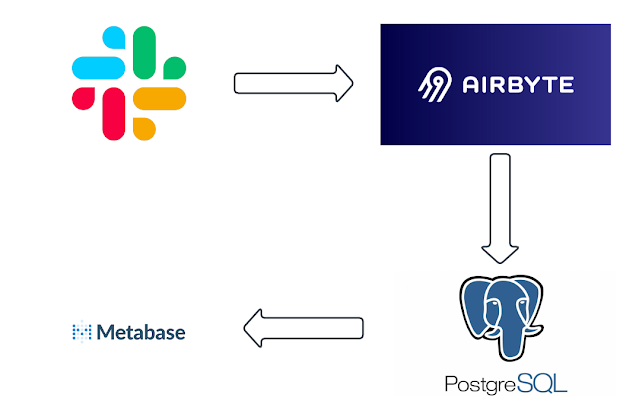
Visualizing your SBOMs via graph...
Introduction
pyspdxtools is a Python library and command-line tool that provides utilities for working with Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) files in the SPDX (Software Package Data Exchange) format. SPDX is a widely adopted standard for documenting the open-source software components used in a project, along with associated metadata such as licenses, copyrights, and relationships between components.
Why Generate a Graph from an SBOM?
Visualizing an SBOM as a graph helps you quickly understand the relationships between components, dependencies, and packages. By generating a graph, you can:
-
- Identify Key Dependencies: Easily spot core libraries or components that are crucial to the software.
- Understand Relationships: Visualize how different packages are connected, including dependencies and sub-dependencies.
With this tutorial, you’ll be able to generate such a graph from your SPDX SBOM using `pyspdxtools`, making it easier to analyze and present your software’s component relationships.
pyspdxtools Installation:
Here’s a step-by-step tutorial to install `pyspdxtools`, set up the required dependencies, and generate a graph from an SPDX SBOM.Prerequisites
- Python 3.7+: Ensure you have Python 3.7 or later installed.
- Pip: Make sure `pip` is installed to manage Python packages.
Step 0: Clone the Repository
$ git clone git@github.com:spdx/tools-python.git
$ cd tools-python
Step 1: Set Up a Virtual Environment (Optional but Recommended)
Create and activate a virtual environment to avoid conflicts with other Python packages.
$ python3 -m venv spdxenv
$ source spdxenv/bin/activate
Step 2: Install `pyspdxtools` and Required Dependencies First, install the base package:
$ pip install .
$ pyspdxtools --help
To generate graphs, you need additional dependencies: `networkx` and `pygraphviz`. Install these using the following command:
$ sudo apt-get install graphviz libgraphviz-dev $ pip install ".[graph_generation]" Step 3: Generate a Graph from Your SPDX SBOM
Before generating the graph, validate your SBOM to ensure it’s correct:
$ pyspdxtools -i <path_to_your_sbom>If there is no output, it means your SBOM is correct.
Now, generate the graph:
$ pyspdxtools -i <path_to_your_sbom> --graph -o output.pngStep 4: View the Generated Graph
After running the command, view the graph using:
$ xdg-open output.png # On Linux or simply double click that file to see the full image.
Example
Suppose you have an SBOM file located at `~/sbom/sbomqs-linux.spdx.sbom.json`. Run the following:
$ pyspdxtools -i ~/sbom/sbomqs-linux.spdx.sbom.json --graph -o sbom_graph.png This will generate a file named `sbom_graph.png` containing the graphical representation of your SBOM.
Finally, open it with:
$ xdg-open sbom_graph.png # Linux Conclusion
This tutorial guides you through installing `pyspdxtools`, setting up the necessary dependencies, and generating a graph from your SBOM. With this, you can easily visualize your SBOM data and gain insights into the relationships between components.






Comments
Post a Comment